The foreign exchange (Forex) market is one of the largest and most liquid financial markets in the world. With daily trading volumes exceeding $6 trillion, it offers ample opportunities for individuals and institutions to trade currencies for profit. If you’re new to Forex or looking to refine your trading strategy, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps and concepts needed to trade in the Forex market successfully.
What is Forex Trading?
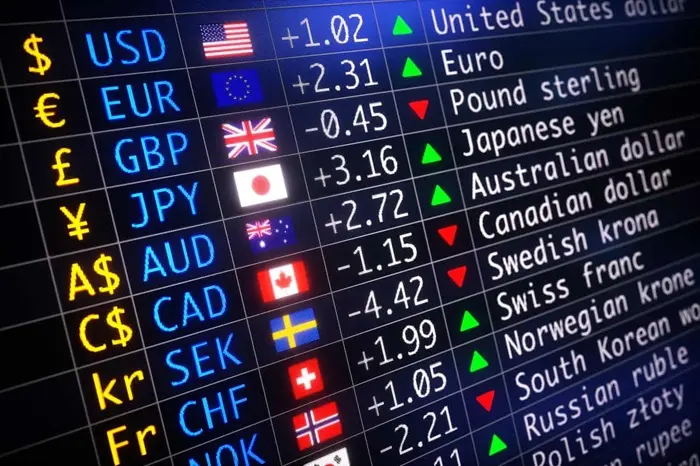
Forex trading, or currency trading, involves buying one currency while simultaneously selling another. Currency pairs are quoted in terms of their exchange rate, which represents the value of one currency relative to another. Forex trading occurs over-the-counter (OTC), meaning it doesn’t take place on a centralized exchange but instead happens directly between buyers and sellers through electronic platforms and networks.
The goal of Forex trading is to profit from changes in currency exchange rates. For example, if you believe the Euro will rise against the US Dollar, you would buy EUR/USD. If the Euro strengthens, you can sell the pair for a profit.
The Basics of Forex Trading
Before jumping into actual trading, it’s important to understand some of the fundamental concepts of Forex trading.
Currency Pairs
Currencies are always quoted in pairs. The first currency in the pair is called the base currency, and the second currency is called the quote currency. For example, in the currency pair EUR/USD, the Euro (EUR) is the base currency, and the US Dollar (USD) is the quote currency.
When you buy EUR/USD, you are buying Euros and selling US Dollars. If the exchange rate increases, you can sell the Euros back for more Dollars, making a profit.
Major Currency Pairs
The major currency pairs are the most traded and liquid pairs in the Forex market. They include:
EUR/USD: Euro/US Dollar
GBP/USD: British Pound/US Dollar
USD/JPY: US Dollar/Japanese Yen
USD/CHF: US Dollar/Swiss Franc
AUD/USD: Australian Dollar/US Dollar
USD/CAD: US Dollar/Canadian Dollar
These pairs have tighter spreads and higher liquidity compared to other currency pairs, making them suitable for beginners.
Minor and Exotic Pairs
In addition to the major pairs, there are minor and exotic currency pairs. Minor pairs do not involve the US Dollar but include other major currencies, such as EUR/GBP (Euro/British Pound). Exotic pairs are made up of a major currency and a currency from an emerging or smaller economy, such as USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira).
Exotic pairs tend to be less liquid and more volatile, making them riskier but potentially more profitable for experienced traders.
Understanding Exchange Rates
The exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of another. For instance, if the exchange rate of EUR/USD is 1.2000, it means that 1 Euro is worth 1.20 US Dollars. Exchange rates fluctuate constantly due to factors like interest rates, economic data, geopolitical events, and market sentiment.
Pips and Lots
When trading in Forex, price movements are measured in pips. A pip stands for “percentage in point” and is the smallest price change that a currency pair can make. For most currency pairs, a pip is equivalent to 0.0001 of the exchange rate.
A lot refers to the size of a trade. Standard lots are typically 100,000 units of the base currency. Smaller sizes include mini lots (10,000 units) and micro lots (1,000 units). The size of your trade determines the potential profit or loss for each pip movement.
How to Get Started with Forex Trading
If you’re new to Forex, the following steps will guide you in getting started with your trading journey.
Step 1: Choose a Reliable Forex Broker
To trade Forex, you need to open an account with a Forex broker. A broker provides you with access to the Forex market through a trading platform. There are many brokers to choose from, so it’s essential to select one that meets your needs in terms of:
Regulation: Ensure the broker is regulated by a reputable financial authority.
Trading Platform: Most brokers offer platforms like MetaTrader 4 (MT4) or MetaTrader 5 (MT5), which are user-friendly and widely used.
Spreads and Fees: Compare the spreads (the difference between the bid and ask price) and commission fees charged by brokers.
Leverage: Brokers offer leverage, allowing you to control larger positions with a smaller deposit. However, leverage increases both potential profits and potential losses, so use it cautiously.
Customer Support: Choose a broker with reliable customer service to assist you when needed.
Step 2: Open a Demo Account
Most Forex brokers offer demo accounts where you can practice trading with virtual money. A demo account allows you to get familiar with the trading platform, understand market movements, and develop a trading strategy without risking real money. It’s highly recommended to use a demo account until you feel confident enough to trade with real capital.
Step 3: Learn and Understand Technical and Fundamental Analysis
To succeed in Forex trading, you must understand both technical and fundamental analysis.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying historical price movements and chart patterns to predict future price movements. Some of the key tools in technical analysis include:
Charts: Use line, bar, or candlestick charts to analyze price movements.
Indicators: These are mathematical calculations based on the price and volume of a currency pair. Common indicators include moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands.
Trendlines: Draw trendlines to identify support and resistance levels, helping you predict potential price reversals.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves analyzing economic data, news, and geopolitical events to determine the intrinsic value of a currency. Key factors that affect currency prices include:
Interest Rates: Central banks set interest rates, which directly affect currency value. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency.
Economic Indicators: Reports such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation data provide insight into the health of a country’s economy.
Political Events: Elections, trade negotiations, and geopolitical tensions can significantly impact currency prices.
Step 4: Develop a Trading Plan
A trading plan is essential for maintaining discipline and managing risk. Your trading plan should include:
Goals: Define your financial objectives and set realistic targets.
Risk Management: Decide how much capital you are willing to risk on each trade. A common rule is to risk no more than 1-2% of your trading capital on any single trade.
Entry and Exit Strategies: Define the conditions under which you will enter and exit a trade. This can be based on technical indicators, chart patterns, or economic news.
Position Sizing: Determine the size of your trades based on your risk tolerance and account size.
Step 5: Start Trading with Real Money
Once you’ve gained enough experience on a demo account, you can begin trading with real money. Start with a small deposit and gradually increase your trading capital as you gain experience. It’s important to stick to your trading plan and avoid emotional decision-making.
Common Forex Trading Strategies
There are several strategies you can use to trade the Forex market. The right strategy for you depends on your trading style, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
Day Trading
Day trading involves opening and closing positions within the same day. Day traders typically look for small price movements and rely on technical analysis to make quick decisions. This strategy requires a high level of attention and quick decision-making skills.
Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days or weeks. Swing traders aim to capture larger price movements and typically use both technical and fundamental analysis to make trading decisions.
Scalping
Scalping involves making numerous small trades throughout the day to capture small price movements. Scalpers typically trade in short time frames, such as 1-minute or 5-minute charts. This strategy requires quick execution and a high level of focus.
Carry Trade
A carry trade involves borrowing a low-interest-rate currency to fund the purchase of a high-interest-rate currency. Traders earn the difference in interest rates, known as the carry, while also benefiting from potential currency appreciation.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
Forex trading is inherently risky, and risk management is essential for long-term success. Here are some risk management strategies to protect your capital:
Stop-Loss Orders: Set stop-loss orders to automatically close a trade if the market moves against you. This helps limit your losses.
Take-Profit Orders: Set take-profit orders to lock in profits once your target price is reached.
Position Sizing: Adjust the size of your trades to match your risk tolerance and account balance.
Diversification: Avoid putting all your capital into one currency pair. Diversifying across different pairs can reduce risk.
Conclusion
Forex trading can be highly rewarding, but it requires a solid understanding of the market, the right tools, and effective risk management strategies. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can start your Forex trading journey with confidence. Remember to practice on a demo account, develop a trading plan, and always trade with caution. The key to success in Forex is continuous learning, discipline, and adapting to changing market conditions.
Related topics: