Bali is a popular tourist destination located in Indonesia, known for its stunning beaches, vibrant culture, and rich history. As a major travel hub, understanding the currency used in Bali and its exchange rate to the United States Dollar (USD) is essential for visitors and businesses involved in trade or tourism. This article will explore Bali’s currency, the factors influencing its exchange rate with the USD, and how it affects both locals and tourists.
Introduction to the Bali Currency
The official currency used in Bali, as well as throughout Indonesia, is the Indonesian Rupiah (IDR). The Rupiah is abbreviated as “Rp” and is issued and regulated by Bank Indonesia, the country’s central bank. While the Indonesian Rupiah is the primary currency, many businesses in Bali, especially those in the tourism industry, may also accept US Dollars (USD). However, the local currency, IDR, is the most commonly used and preferred form of payment.
Indonesia has a complex currency system with bills and coins in different denominations. As of recent years, the exchange rate between the Indonesian Rupiah and the US Dollar has fluctuated based on economic and market factors.
Understanding the Bali Currency to USD Exchange Rate
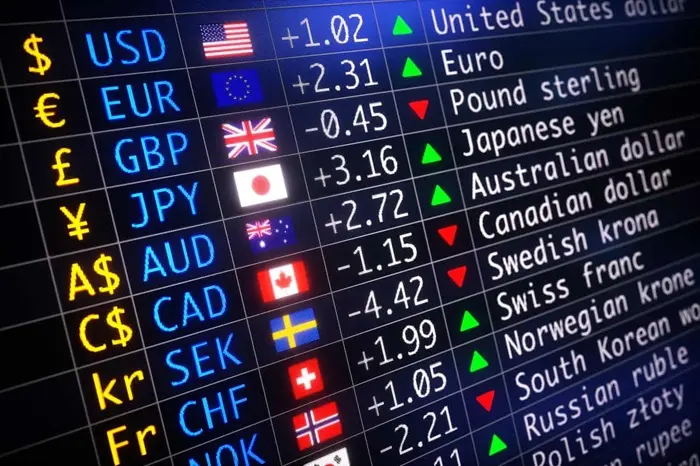
The exchange rate between the Indonesian Rupiah (IDR) and the US Dollar (USD) represents the value of one US Dollar in terms of Rupiah. For example, if the exchange rate is 1 USD = 15,000 IDR, it means that for every US Dollar, you will receive 15,000 Indonesian Rupiah. The exchange rate is not fixed and can fluctuate daily based on various economic factors.
The rate of exchange can differ depending on where and how the currency is exchanged. Currency exchange services in Bali, such as at banks, exchange bureaus, or hotels, might offer different rates, and tourists are encouraged to compare rates to get the best value for their money. Understanding how the exchange rate works can help travelers make informed decisions about currency exchange and budgeting for their trip.
Why Exchange Rates Matter in Bali
The exchange rate between the IDR and USD is an important consideration for both tourists visiting Bali and businesses that engage in trade. For tourists, the exchange rate determines how much local currency they will receive when converting their US Dollars. A favorable exchange rate means that tourists will have more purchasing power during their stay.
For businesses, the exchange rate affects the cost of imports and exports. Bali’s economy relies heavily on tourism and international trade, so fluctuations in the IDR to USD exchange rate can impact business profits. It is essential for local businesses to keep track of the exchange rate to ensure they maintain competitive pricing and manage costs effectively.
Factors Influencing the IDR to USD Exchange Rate
Several factors influence the value of the Indonesian Rupiah in relation to the US Dollar. Understanding these factors is key to grasping how and why the exchange rate fluctuates.
1. Economic Conditions in Indonesia
Indonesia’s economic health plays a significant role in determining the value of the Rupiah. Strong economic growth, stable inflation rates, and low unemployment levels generally support the value of the local currency. Conversely, economic downturns, rising inflation, or political instability can weaken the Rupiah, leading to a higher exchange rate (more IDR per USD).
Indonesia is one of the largest economies in Southeast Asia, with key industries including agriculture, mining, manufacturing, and tourism. The performance of these sectors, along with economic policies, greatly influences the currency’s strength.
2. US Economic Conditions
The strength of the US Dollar is another important factor that impacts the exchange rate between the IDR and USD. When the US economy is performing well, the USD tends to appreciate against other currencies, including the Indonesian Rupiah. Conversely, when the US economy experiences a slowdown, the USD may weaken, leading to changes in the exchange rate.
Global events, such as shifts in the US Federal Reserve’s monetary policy or trade negotiations, can also affect the value of the USD and, consequently, the IDR to USD exchange rate.
3. Inflation Rates
Inflation rates in Indonesia have a direct effect on the value of the Rupiah. When inflation in Indonesia is high, the purchasing power of the Rupiah decreases, which can lead to a depreciation of the currency. On the other hand, low inflation rates can support the value of the currency, making it more attractive to investors and foreign traders.
Inflationary pressures can be caused by a variety of factors, such as an increase in the cost of essential goods, energy prices, or changes in domestic demand. Central banks, such as Bank Indonesia, often use monetary policies to manage inflation and stabilize the value of the Rupiah.
4. Commodity Prices
Indonesia is a major producer of natural resources and commodities, including palm oil, coal, rubber, and coffee. The global prices of these commodities can impact the value of the Rupiah. When commodity prices rise, Indonesia’s export revenues increase, leading to a stronger currency as foreign buyers purchase more Indonesian goods. Conversely, when commodity prices fall, the Rupiah may weaken.
Since Bali’s economy heavily relies on tourism, fluctuations in commodity prices can affect the broader economic climate, influencing the currency exchange rate and purchasing power.
5. Foreign Investment and Trade Balances
Indonesia’s trade balance, or the difference between its exports and imports, also affects the IDR/USD exchange rate. When Indonesia exports more goods and services than it imports, the country experiences a trade surplus, which can strengthen the Rupiah. On the other hand, a trade deficit, where imports exceed exports, can lead to a weaker currency.
Foreign investment is another crucial factor. When foreign investors are confident in Indonesia’s economic prospects, they are more likely to invest in the country, which can lead to increased demand for the Rupiah. This demand can cause the value of the IDR to appreciate.
6. Political Stability and Government Policies
Political stability is essential for maintaining investor confidence. When Indonesia experiences political unrest, it can lead to a decrease in foreign investment and a depreciation of the Rupiah. Political events, such as elections, changes in leadership, or shifts in government policy, can create uncertainty that impacts the exchange rate.
Similarly, the Indonesian government’s policies regarding trade, tourism, foreign investment, and monetary regulation can also influence the value of the Rupiah. For example, government policies that encourage foreign investment can boost the currency, while protectionist policies may reduce demand for the local currency.
Impact of Exchange Rate Fluctuations on Bali’s Economy
Fluctuations in the IDR to USD exchange rate have significant implications for various sectors of Bali’s economy. Below are some of the ways in which exchange rate changes affect businesses, consumers, and the tourism industry in Bali.
1. Impact on Tourism
Bali is one of the world’s most popular tourist destinations, attracting millions of international visitors every year. The exchange rate between the IDR and USD plays a critical role in shaping the tourism industry. A favorable exchange rate (where the USD is strong relative to the Rupiah) encourages more tourists to visit Bali, as their money goes further in terms of local purchasing power.
Tourists may find that they can stay in higher-end hotels, dine at upscale restaurants, and participate in activities they might not have been able to afford if the exchange rate were less favorable. This leads to increased demand for services, benefiting local businesses.
However, when the IDR depreciates significantly against the USD, it can result in higher prices for goods and services in Bali, which might discourage tourists from spending as freely as they would in times of a stronger Rupiah. Consequently, businesses in the hospitality and tourism industries must adjust their pricing strategies to account for exchange rate fluctuations.
2. Impact on Importers and Exporters
Businesses involved in importing goods into Bali may be affected by fluctuations in the exchange rate. A weaker Rupiah makes imports more expensive for Indonesian businesses, potentially raising the costs of goods and services. For example, if a business imports foreign goods or raw materials, the cost of these imports may increase as the exchange rate rises.
Conversely, businesses that export products to other countries, including the United States, may benefit from a stronger Rupiah, as their goods become more affordable in international markets. This can lead to increased sales and profits for exporters, benefiting the broader Indonesian economy.
3. Impact on Local Consumers
For local consumers in Bali, changes in the exchange rate can affect their purchasing power. A weaker Rupiah means that consumers may have to spend more to purchase imported goods, which could lead to inflation. On the other hand, when the Rupiah is stronger, imported goods become more affordable, which can lower prices and increase consumer spending.
Additionally, inflationary pressures caused by exchange rate fluctuations can lead to higher living costs for residents of Bali. Consumers may find that everyday expenses such as food, fuel, and utilities become more expensive, impacting their overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the Bali currency to USD exchange rate is essential for anyone traveling to or doing business in Bali. The Indonesian Rupiah is the primary currency in Bali, and the value of the IDR relative to the US Dollar has significant implications for the tourism industry, trade, and consumer purchasing power. Several factors influence the IDR/USD exchange rate, including economic conditions, inflation rates, commodity prices, and political stability.
For tourists visiting Bali, a favorable exchange rate can make their experience more affordable and enjoyable, while fluctuations in the exchange rate can affect businesses in various industries. Whether you are a traveler, investor, or business owner, it is crucial to stay informed about the current exchange rates to make informed decisions and navigate the economic landscape effectively.
By monitoring the exchange rate and understanding the factors that drive it, tourists and businesses can better manage costs and maximize opportunities in Bali. The dynamic relationship between the Indonesian Rupiah and the US Dollar highlights the interconnectedness of global economies and the importance of understanding currency markets in an increasingly globalized world.
Related topics: