The exchange rate between the United States Dollar (USD) and the South African Rand (ZAR) is a key indicator in global financial markets. This rate reflects the value of one currency against another and is vital for international trade, investment, and economic relations. Understanding how this exchange rate functions can help businesses, investors, and individuals make informed decisions. This article will explain the USD to ZAR exchange rate, factors that influence it, and how it impacts various stakeholders.
Understanding the USD to ZAR Exchange Rate
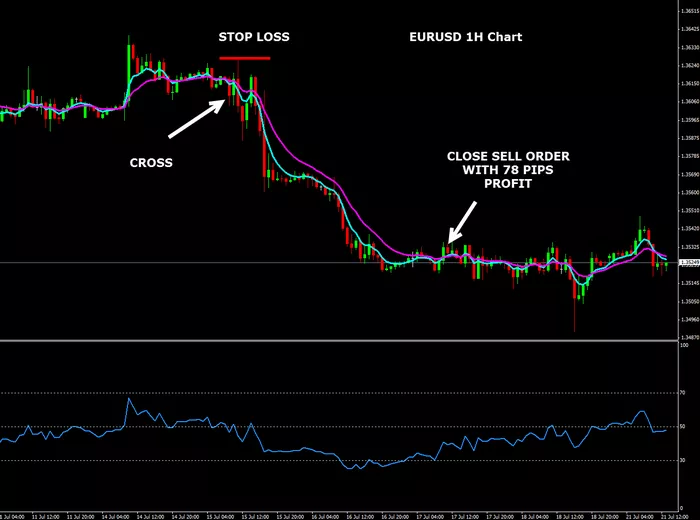
The USD to ZAR exchange rate refers to the value of one US dollar in terms of South African Rand. In simple terms, it tells you how many rands you can get for one dollar. This exchange rate is determined by various economic, political, and market factors. It is subject to change daily, depending on market conditions, as currencies are traded on the foreign exchange market (Forex).
How is the USD to ZAR Exchange Rate Calculated?
The USD to ZAR exchange rate is calculated based on the supply and demand for both currencies in the international market. If there is higher demand for the US dollar, its value will rise relative to the South African Rand. Conversely, if demand for the Rand increases, its value will strengthen compared to the USD. These fluctuations are impacted by several key factors such as economic reports, political stability, and market sentiment.
What Does the USD to ZAR Exchange Rate Mean for Individuals?
For individual travelers, businesses, or investors, understanding the USD to ZAR rate is crucial. For example, tourists traveling from the United States to South Africa will need to exchange their dollars for rand. If the rate is favorable, they will get more rand for their dollars, making their trip more affordable. Similarly, for businesses that deal in international trade, understanding the exchange rate allows them to better plan for costs and profits when conducting transactions between countries.
Factors Influencing the USD to ZAR Exchange Rate
1. Economic Data and Indicators
Economic data plays a major role in influencing exchange rates. Reports such as GDP growth, employment figures, inflation rates, and trade balances affect the strength of a currency. For example, if the United States reports strong economic growth, the demand for the US dollar may increase, pushing up the USD to ZAR exchange rate. Conversely, if South Africa’s economy shows signs of growth, it could lead to a stronger Rand.
Inflation Rates
Inflation is one of the most significant economic indicators that affect currency strength. If inflation in the United States rises significantly, the purchasing power of the USD declines, potentially leading to a weaker dollar against other currencies, including the Rand. On the other hand, if South Africa experiences low inflation, the Rand may strengthen against the USD.
Interest Rates
Interest rates set by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (for the US) and the South African Reserve Bank (SARB), influence currency values. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, which can strengthen a currency. If the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it may result in a stronger USD as investors seek higher returns in US-based assets.
2. Political Stability
Political events and decisions can have a significant impact on exchange rates. For instance, any political instability or uncertainty in South Africa may lead to a weaker Rand as investors seek safer assets, such as the US dollar. Similarly, political changes in the US can influence the strength of the dollar, depending on how investors perceive the new political landscape.
Elections and Government Policies
Elections in both the United States and South Africa can result in volatility in exchange rates. For example, if there is uncertainty surrounding election outcomes or government policies that may affect trade relations, investors may move their money away from the perceived riskier currency. This shift in investment can lead to changes in the USD to ZAR exchange rate.
3. Global Commodity Prices
South Africa is a major exporter of commodities like gold, platinum, and other minerals. As such, fluctuations in global commodity prices can affect the value of the South African Rand. When commodity prices are high, South Africa’s export revenues increase, which can strengthen the Rand. However, when commodity prices fall, the Rand may weaken, leading to a higher USD to ZAR exchange rate.
Oil Prices
The price of oil is another key factor that impacts the ZAR. South Africa imports most of its oil, and when oil prices rise, it increases the country’s trade deficit. This may lead to a weakening of the Rand and a higher USD to ZAR exchange rate.
4. Market Sentiment and Speculation
The foreign exchange market is often influenced by investor sentiment and speculation. Traders make decisions based on news, forecasts, and market rumors, which can cause short-term fluctuations in the USD to ZAR exchange rate. If traders believe that the US economy will outperform the South African economy, they may buy USD in anticipation of a stronger dollar.
Global Financial Events
Global financial events, such as economic crises or major geopolitical tensions, can create uncertainty in the markets. This uncertainty may lead to a flight to safety, where investors move their capital into safer assets like the US dollar. As a result, the USD could strengthen against the ZAR in times of global financial instability.
The Role of Central Banks in USD to ZAR Exchange Rate
Central banks play a crucial role in influencing currency values. The US Federal Reserve (Fed) and the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) have policies that directly affect the exchange rate between the USD and ZAR. These central banks adjust interest rates, engage in open market operations, and sometimes intervene in the foreign exchange markets to stabilize their respective currencies.
Federal Reserve’s Impact on the USD
The Federal Reserve is a major player in the global financial system, and its monetary policy decisions can have a profound impact on the value of the USD. When the Fed raises or lowers interest rates, it can influence the demand for the US dollar. For example, a higher interest rate in the US typically leads to a stronger dollar as it attracts foreign investment.
South African Reserve Bank’s Role in the ZAR
The South African Reserve Bank (SARB) has a similar role in managing the value of the Rand. SARB’s monetary policy decisions, including interest rate adjustments, can influence the USD to ZAR exchange rate. For instance, if the SARB raises interest rates to curb inflation, it could lead to a stronger Rand.
Effects of USD to ZAR Exchange Rate on Trade
The USD to ZAR exchange rate has a significant impact on international trade between the United States and South Africa. A stronger US dollar means that South African goods become more expensive for American consumers, potentially reducing demand for South African exports. Conversely, when the Rand weakens against the dollar, South African exports may become more competitive in the global market, but imports may become more expensive.
Import and Export Dynamics
For businesses involved in importing goods from the United States, a higher USD to ZAR exchange rate can increase costs, potentially reducing profit margins. On the other hand, South African exporters benefit from a weaker Rand because their goods become cheaper for international buyers, boosting demand.
How Investors Can Benefit from the USD to ZAR Exchange Rate
Investors who trade currencies can benefit from fluctuations in the USD to ZAR exchange rate. Forex traders buy and sell currencies in anticipation of future changes in exchange rates. By correctly predicting movements in the USD to ZAR rate, traders can make profits. However, currency trading also involves risk, and traders need to stay informed about global economic and political developments that could affect the exchange rate.
Hedging Against Currency Risk
Companies and investors who have exposure to foreign exchange risk may use hedging strategies to protect against fluctuations in the USD to ZAR rate. For example, a South African company that imports goods from the United States may use forward contracts to lock in a favorable exchange rate, thus reducing the risk of future exchange rate fluctuations.
Conclusion
The USD to ZAR exchange rate is influenced by a variety of factors, including economic data, political stability, commodity prices, and market sentiment. Understanding these factors is essential for individuals, businesses, and investors who deal with the US Dollar and the South African Rand. While the exchange rate can fluctuate, its value reflects the relative economic strength of both the United States and South Africa. By monitoring the key drivers of the USD to ZAR rate, stakeholders can make informed decisions that maximize their financial interests.
Related topics: