The foreign exchange (forex or FX) market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. With over $6 trillion in daily trading volume, it offers countless opportunities for traders to profit from currency fluctuations. However, navigating the complexities of forex trading can be overwhelming for beginners. Whether you are looking to trade as a hobby or make a career out of it, learning forex requires a structured approach, dedication, and a thorough understanding of the market.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the essential steps and strategies on how to learn forex. From understanding the basics to mastering advanced trading techniques, this article will help you take your first steps into the forex world with confidence.
Understanding Forex: The Basics
Before diving into the strategies and technicalities of forex trading, it is crucial to understand the basics of the market itself. Forex refers to the global marketplace where currencies are traded. Unlike other financial markets such as stocks or commodities, forex trading takes place 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing traders from around the world to participate at any time.
What is Forex Trading?
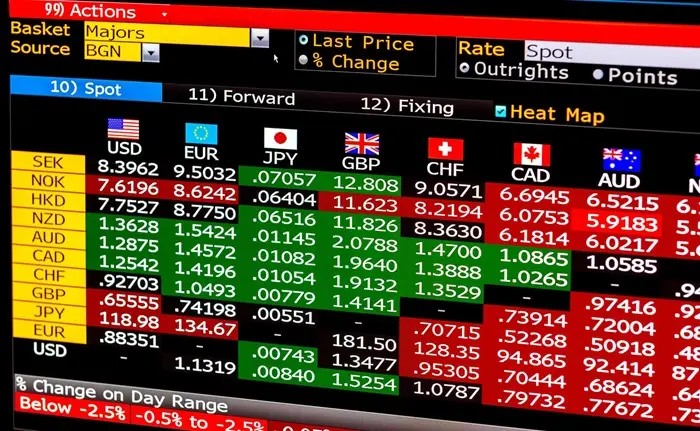
Forex trading involves buying one currency while simultaneously selling another. Currencies are always traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, and USD/JPY. The first currency in the pair is called the “base currency,” while the second is called the “quote currency.” The value of the currency pair is determined by how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency.
For example, in the EUR/USD currency pair, the EUR is the base currency, and the USD is the quote currency. If the exchange rate is 1.20, it means that 1 Euro is equivalent to 1.20 US Dollars.
Major Currency Pairs
In the forex market, currencies are grouped into several categories based on their trading volume. The most commonly traded currency pairs are called “major pairs” and include:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar)
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen)
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar)
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc)
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar)
- USD/CAD (US Dollar/Canadian Dollar)
These pairs represent the world’s largest economies and are the most liquid, meaning they have tight spreads and lower volatility.
Why Trade Forex?
Forex trading offers several advantages that appeal to investors and traders worldwide. Some of the primary reasons people choose to trade forex include:
Liquidity: With a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion, the forex market offers high liquidity, making it easy to enter and exit trades.
24-Hour Market: The forex market operates around the clock, providing flexibility for traders in different time zones.
Leverage: Forex brokers often offer high leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital.
Low Transaction Costs: Many forex brokers offer low spreads, making it cheaper to trade compared to other markets like stocks or futures.
Steps to Learn Forex
Learning forex requires a methodical approach. It is essential to start with the basics and gradually progress to more advanced topics. Below are the key steps that will help you learn forex successfully.
Step 1: Learn the Basics of Forex Trading
The first step in learning forex is to build a strong foundation by understanding the fundamental concepts of the market. This includes familiarizing yourself with key terminology, such as:
Pip: The smallest unit of measurement in forex trading, representing a change in value for a currency pair.
Lot: A unit of measurement used to indicate the size of a trade. A standard lot is equivalent to 100,000 units of the base currency.
Spread: The difference between the bid (buy) and ask (sell) price of a currency pair.
Leverage: A tool that allows traders to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital.
Margin: The amount of money required to open a leveraged position.
There are many resources available online, including articles, books, and video tutorials, that explain these concepts in more detail. Some free platforms, such as BabyPips, offer beginner-friendly courses that cover the fundamentals of forex trading.
Step 2: Open a Demo Account
Once you understand the basics of forex trading, it is time to practice. Opening a demo account with a reputable forex broker is the best way to learn how to trade without risking real money. A demo account allows you to trade in real market conditions using virtual funds.
Most forex brokers offer demo accounts, and they usually come with all the tools and features available on a live account. This gives you the opportunity to experiment with different trading strategies, test out technical indicators, and get a feel for the platform’s user interface.
Step 3: Choose a Reliable Forex Broker
Selecting a reliable forex broker is one of the most important decisions you will make as a trader. A good broker will provide you with the necessary tools, resources, and support to help you succeed in the forex market. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a broker:
Regulation: Ensure the broker is regulated by a reputable financial authority, such as the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), the US Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), or the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC).
Trading Platform: Choose a broker that offers a user-friendly and robust trading platform, such as MetaTrader 4 or MetaTrader 5.
Spreads and Fees: Compare the spreads and commissions charged by different brokers. Lower spreads will reduce your trading costs.
Customer Support: Choose a broker that offers responsive customer support in case you need assistance.
Leverage and Margin: Look for a broker that offers reasonable leverage and margin policies, keeping in mind the risks associated with using leverage.
Step 4: Understand Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a crucial skill for forex traders. It involves analyzing historical price movements, chart patterns, and technical indicators to predict future price movements. Technical analysis can help you identify trends, entry and exit points, and potential market reversals.
Some of the most popular technical indicators include:
Moving Averages: Used to smooth out price data and identify trends.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the strength of a price move and helps identify overbought or oversold conditions.
Bollinger Bands: Measures volatility and helps identify overbought or oversold conditions.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): A trend-following momentum indicator.
Learning how to read and interpret charts, as well as understanding key patterns like support and resistance levels, is essential for successful forex trading.
Step 5: Learn Fundamental Analysis
In addition to technical analysis, fundamental analysis is another essential tool for forex traders. Fundamental analysis involves evaluating the economic, social, and political factors that influence currency prices. This includes studying economic indicators such as:
Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can have a significant impact on currency values.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): A strong GDP indicates a healthy economy and can lead to a stronger currency.
Inflation Rates: Inflation affects the purchasing power of a currency and can influence central bank policies.
Employment Data: Unemployment rates and job creation figures are important economic indicators.
By understanding these key economic factors, you can make more informed decisions about which currencies to trade and when to enter or exit the market.
Step 6: Develop a Trading Strategy
Developing a well-defined trading strategy is crucial to success in the forex market. Your strategy should take into account your risk tolerance, trading style, and market conditions. There are several types of trading strategies, including:
Scalping: A short-term strategy that involves making quick trades to capture small price movements.
Day Trading: A strategy where traders open and close positions within the same trading day.
Swing Trading: A medium-term strategy where traders hold positions for several days to take advantage of price swings.
Position Trading: A long-term strategy where traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years.
Each strategy has its advantages and disadvantages, and the right strategy for you will depend on your personal preferences and risk tolerance.
Step 7: Practice Risk Management
Risk management is a crucial aspect of forex trading. Successful traders always manage their risk by using techniques such as:
Stop-Loss Orders: A stop-loss order automatically closes a position when the market moves against you by a predetermined amount. This helps limit potential losses.
Take-Profit Orders: A take-profit order automatically closes a position when the market reaches a predetermined profit level.
Position Sizing: Properly sizing your positions ensures that you are not overexposed to any single trade.
By practicing sound risk management, you can minimize losses and protect your capital.
Step 8: Continuously Learn and Improve
The forex market is constantly evolving, and successful traders are always learning and adapting to new conditions. Stay up to date with the latest news and trends in the forex market, and continuously refine your trading skills.
Reading books, taking online courses, attending webinars, and following forex experts on social media can all help you expand your knowledge and improve your trading abilities.
Conclusion
Learning forex trading requires patience, dedication, and a structured approach. By understanding the basics of the market, practicing with a demo account, and developing a solid trading strategy, you can begin your journey toward becoming a successful forex trader.
Remember, forex trading involves risk, and it is essential to continuously educate yourself and practice sound risk management techniques. With time and experience, you can improve your skills and potentially profit from the world’s largest financial market.
Related topics: